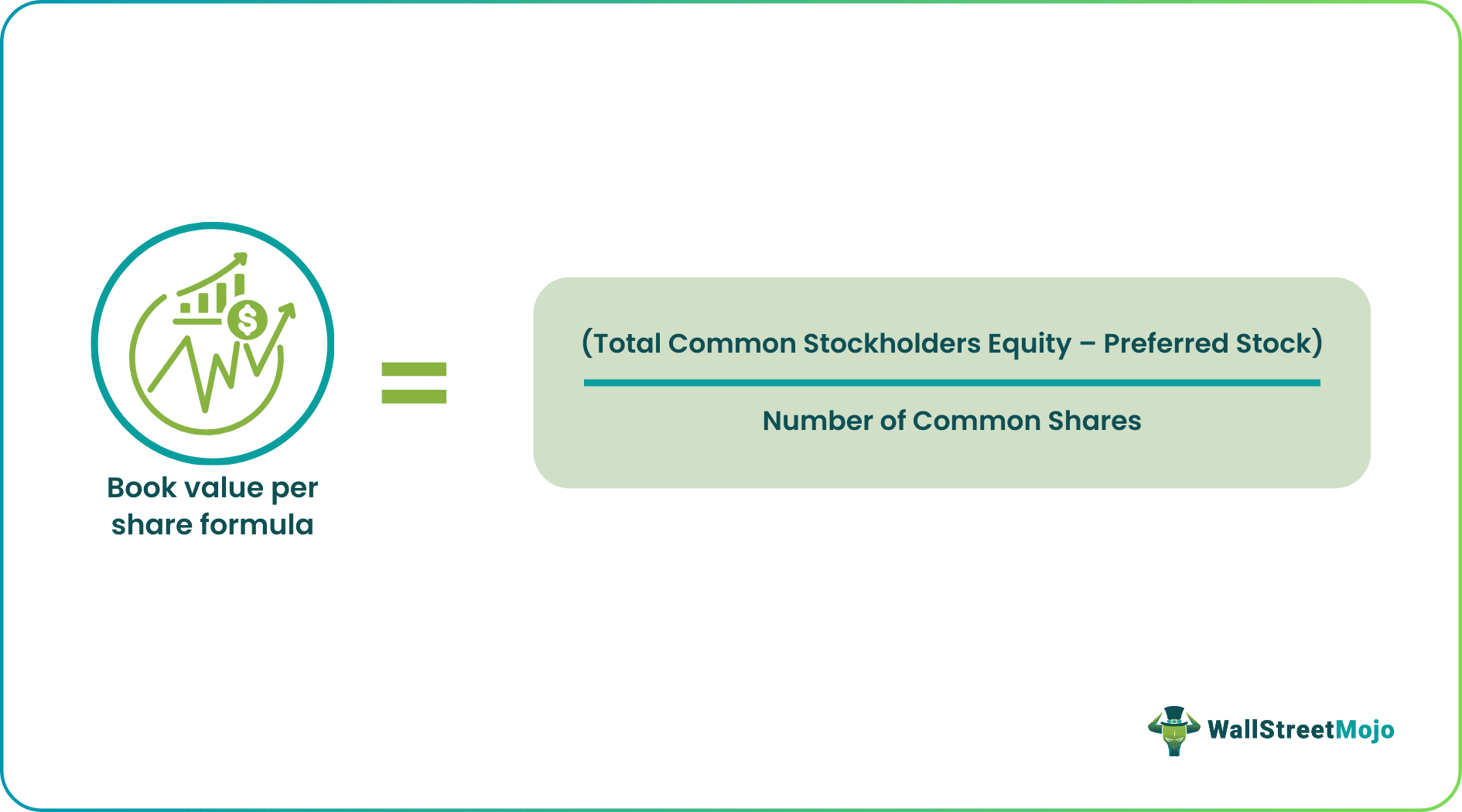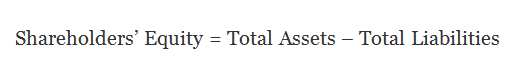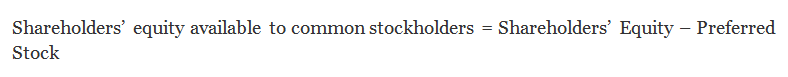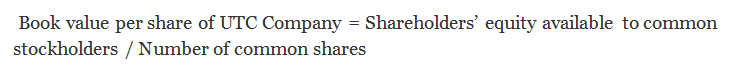Table Of Contents
Key Takeaways
- The "Book Value Per Share formula" calculates the value that each outstanding common share holds by dividing the total book value by the number of common shares.
- The book-to-market ratio serves as a valuable tool for assessing equity. It entails a comparison between the market value of equity and either earnings or book value.
- When determining the book value per share, begin by subtracting the preferred stock from the shareholders' equity to ascertain the equity accessible to common stockholders.
Explanation
The above book value per share formula has two parts.
The first part is to find out the equity available to the common stockholders. You may ask why we deduct the preferred stock and average outstanding common stock. We deduct preferred stock from the shareholders’ equity because preferred shareholders are paid first after the debts are paid off.
- Book Value = Shareholders Equity - Preferred Stock
- And Shareholder's equity = Total Assets - Total Liabilities.
The second part divides the shareholders' equity available to equity stockholders by the number of common shares.
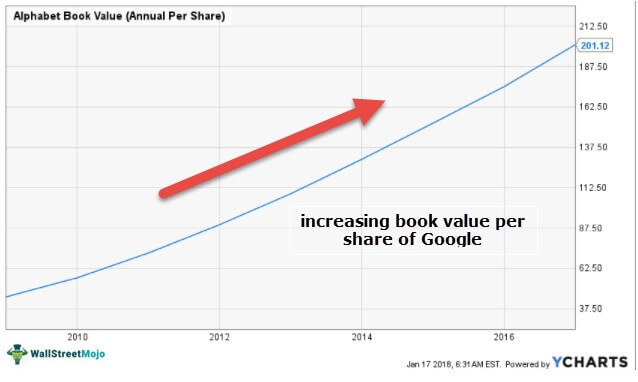
In the below graph, we see the book value of Google for the past ten years. The book value of Google in 2008 was $44.90 per share and had increased by 348% to $201.12 per share by the end of 2016.
Example
Let's take a simple book value per share example -
UTC Company has the following information –
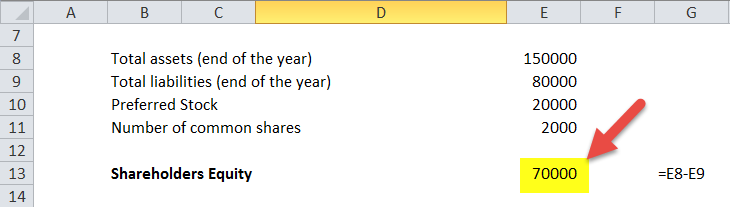
- Total assets at the end of the year - $150,000
- Total liabilities at the end of the year - $80,000
- Preferred Stock - $20,000
- Number of common shares – 2000 shares
Our job is to find out the book value of UTC Company.
The first part of our calculation would be to find out the total shareholders’ equity available to common shareholders and preferred stockholders.
To do that, we need to use the following formula.
- Shareholders' Equity = Total Assets – Total Liabilities;
- Or, Shareholders’ Equity = $150,000 - $80,000 = $70,000.
We need to calculate how much shareholders' equity is available to the common stockholders.
We need to deduct the preferred stocks from the shareholders' equity to do that.
- Shareholders' equity available to common stockholders = Shareholders' Equity – Preferred Stock
- Or, Shareholders’ equity available to common stockholders = $70,000 - $20,000 = $50,000.
We need to divide the shareholders' equity available to common stockholders by the number of common shares.
- Book Value per share formula of UTC Company = Shareholders' equity available to common stockholders / Number of common shares
- BVPS = $50,000 / 2000 = $25 per share.
Uses of BVPS
Investors need to look at both the book value and market value of the share. If the investors can find out the book value of common stocks, they will be able to figure out whether the market value of the share is worth it.
For example, if the BVPS is $20 per share and the market value of the same common share is $30 per share, the investor can determine the ratio of price to book value as = Price / Book Value = $30 / $20 = 1.5.
At the same time, we use book value in the case of the ROE formula when we calculate the ROE per share.
If we look at the ROE per share formula, we would be able to understand it –
ROE per share = Net Income per Share / Book Value per Share
Here, net income per share is also called EPS.